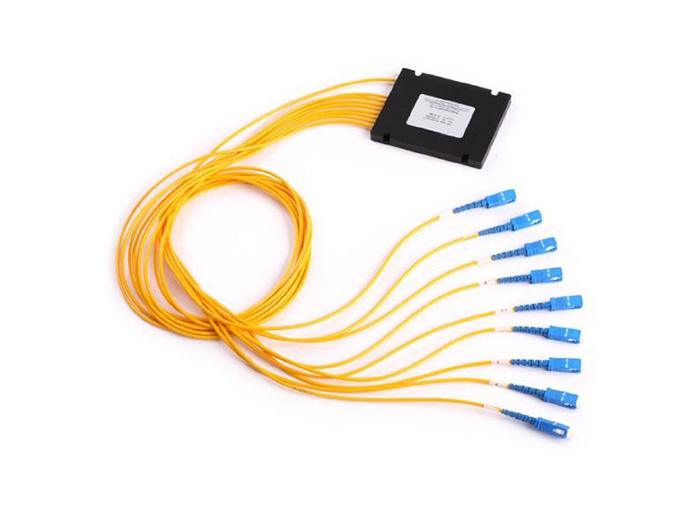
A fiber splitter is a passive optical device that divides a single optical fiber signal into multiple separate signals. These devices are crucial for distributing signals in passive optical networks (PONs) and are widely used in Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) and other fiber optic access networks. Splitters work by using phenomena like refraction and diffraction to split light into multiple paths without requiring external power.
Types of fiber splitters
• Planar Lightwave Circuit (PLC) Splitters: These are based on planar lightwave circuit technology, which uses photolithography to create optical waveguides on a substrate. PLC splitters offer a high degree of splitting (up to 1:64 or more) and have a wide wavelength range, making them suitable for many applications.
• Fused Biconical Taper (FBT) Splitters: Made by fusing and tapering two or more optical fibers together, FBT splitters are a more traditional and cost-effective method for smaller-scale applications. The splitting ratio is customized by controlling the length of the taper.
How they work
• Optical signals enter the splitter through a single input fiber.
• Inside the device, the light is split by a special optical component, such as a PLC chip or a fused fiber structure.
• The light is then distributed to multiple output fibers.
• The "passive" nature means the splitter does not need power to operate; it simply redirects the light.

www.jingkon.com
Ningbo Jingkon Optical Communication Co., Ltd.