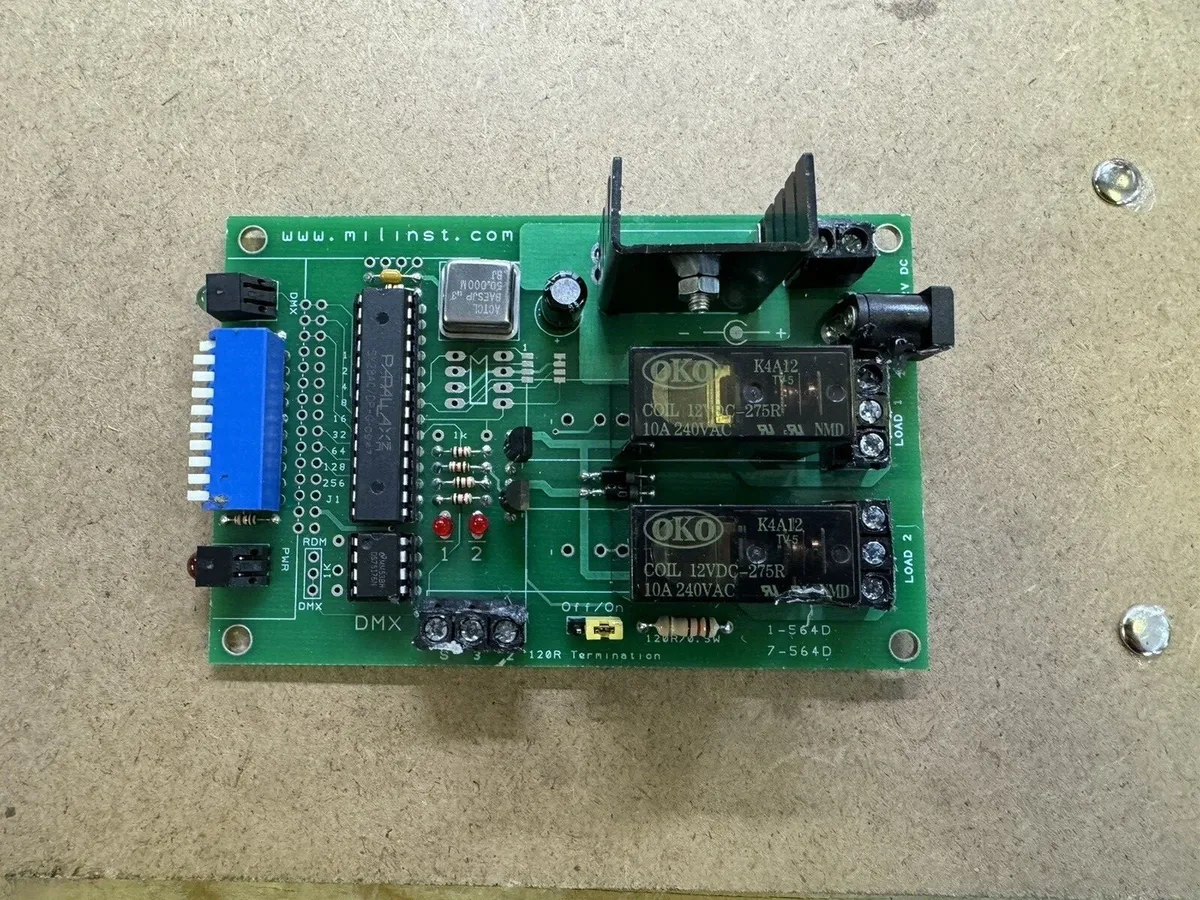
In the realm of industrial automation, two key components play a pivotal role in controlling electrical circuits: Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and mechanical relays. While both serve the purpose of controlling electrical systems, they differ significantly in terms of functionality, flexibility, and efficiency. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of these two control devices, highlighting their differences and shedding light on their respective advantages and disadvantages.
- Functionality:
Mechanical Relays:
Mechanical relays are electromechanical devices that use an electromagnetic coil to open or close electrical contacts. They are primarily used for simple control tasks and are known for their reliability and robustness. However, they lack the ability to perform complex logic operations and require additional components for advanced control functions.
PLCs:
PLCs, on the other hand, are digital computers specifically designed for industrial control applications. They offer a wide range of functionalities, including advanced logic operations, data processing, and communication capabilities. PLCs can execute complex control algorithms, handle multiple inputs and outputs simultaneously, and integrate seamlessly with other automation systems.
- Flexibility:
Mechanical Relays:
Mechanical relays are static devices with fixed wiring connections, making them less flexible in terms of reconfiguration and adaptation to changing requirements. Modifying the control logic often involves rewiring, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Additionally, mechanical relays have limited memory capacity, restricting the number of control sequences they can handle.
PLCs:
PLCs excel in flexibility, allowing users to modify control logic through programming languages like ladder logic or structured text. This enables quick and easy reconfiguration without the need for physical rewiring. Moreover, PLCs offer ample memory capacity, enabling the execution of complex control sequences and the storage of vast amounts of data.
- Efficiency:
Mechanical Relays:
Mechanical relays consume significant power due to the coil energization required to maintain contact positions. This continuous power consumption can lead to increased energy costs and heat generation. Additionally, mechanical relays have slower response times, limiting their suitability for high-speed applications.
PLCs:
PLCs are designed to optimize energy efficiency by utilizing solid-state components. They consume less power, resulting in reduced energy costs and heat dissipation. Furthermore, PLCs offer faster response times, making them ideal for time-critical applications that require rapid decision-making and precise control.
Conclusion:
In summary, the distinction between PLCs and mechanical relays lies in their functionality, flexibility, and efficiency. While mechanical relays are reliable and suitable for simple control tasks, PLCs offer advanced functionalities, flexibility in reconfiguration, and improved efficiency. The choice between the two depends on the complexity of the control system, the need for flexibility, and the desired level of efficiency. By understanding these differences, engineers and automation professionals can make informed decisions when selecting the appropriate control device for their specific applications.